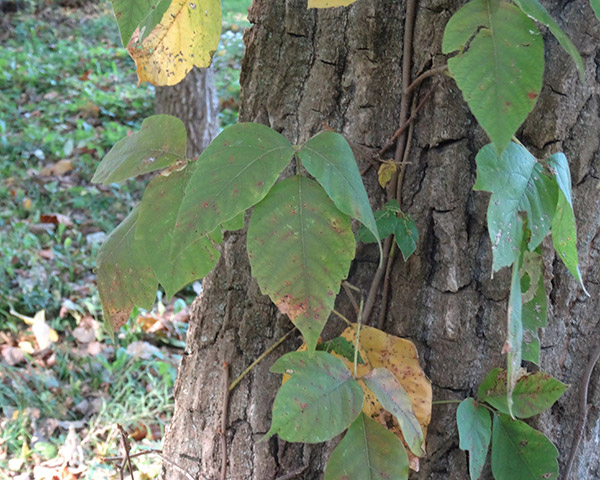
Family: Anacardiaceae
This plant can be found nearly anywhere in the continental United States. In Ohio, it usually grows as a woody vine that climbs up a tree trunk. But it can also spread along the ground, especially in the vicinity of an established vine. The roots of the vine grow under the ground and often sprout up to form to what look like new plants.
Poison ivy is very common in the deciduous forests of Ohio, but it is sometimes confused with other plants. Poison ivy is most commonly confused with is Virginia creeper. Both of these plants are climbing vines with compound leaves. But Virginia creeper usually has five-toothed leaflets while poison ivy has three. Many times the leaves of poison ivy will look withered and discolored, especially later in the growing season. Often you can see little growths on the leaves along with discoloration.
"Leaves of three, let it be."
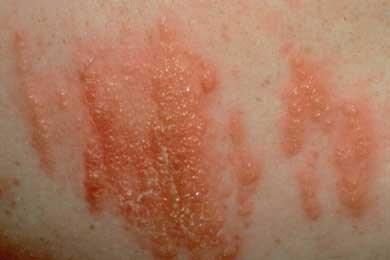
Beware: All parts of this plant can cause an allergic reaction to someone who is sensitive to it. If you are allergic and come in contact with poison ivy, you can develop an itchy rash that will often ooze and spread. Jewelweed, found almost anywhere in Ohio, can be used by some people to relieve minor symptoms. But severe cases often require medical treatment. The vine is not poisonous to other animals, and the berries are often eaten by birds who end up dispersing the seeds over large areas.
Poison ivy skin reaction
References:
http://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?kempercode=l490
http://www.friendsofthewildflowergarden.org/pages/plants/wildgrape.html